Microcertifications vs Exam Marks: A Better Path

Why Exam Marks Are Meaningless: We Should Focus on Proof of Learning Through Microcertifications and Online Portfolios In today’s fast-paced world, the traditional education system, with its heavy reliance on exam marks, is increasingly seen as inadequate for preparing students for real-world challenges. As we move further into the digital age, the focus is shifting […]
ApniPathshala: Enhancing Computer Literacy for Better Education in India
Discover how ApniPathshala is transforming education in India through the power of computer literacy, one student at a time.
10 Best Learning Methods To Maximize Kids’ Growth

Community-based learning pods are revolutionizing education by offering a unique and dynamic learning environment. Unlike traditional schools, pods can tailor their approach to each student, fostering a love of learning and maximizing their potential. This blog explores ten powerful teaching methods that can be implemented in your learning pod: 1. Flipped Classrooms: Learning at Your […]
Unlocking Potential: The Crucial Role of Peer Learning in Educational Centers
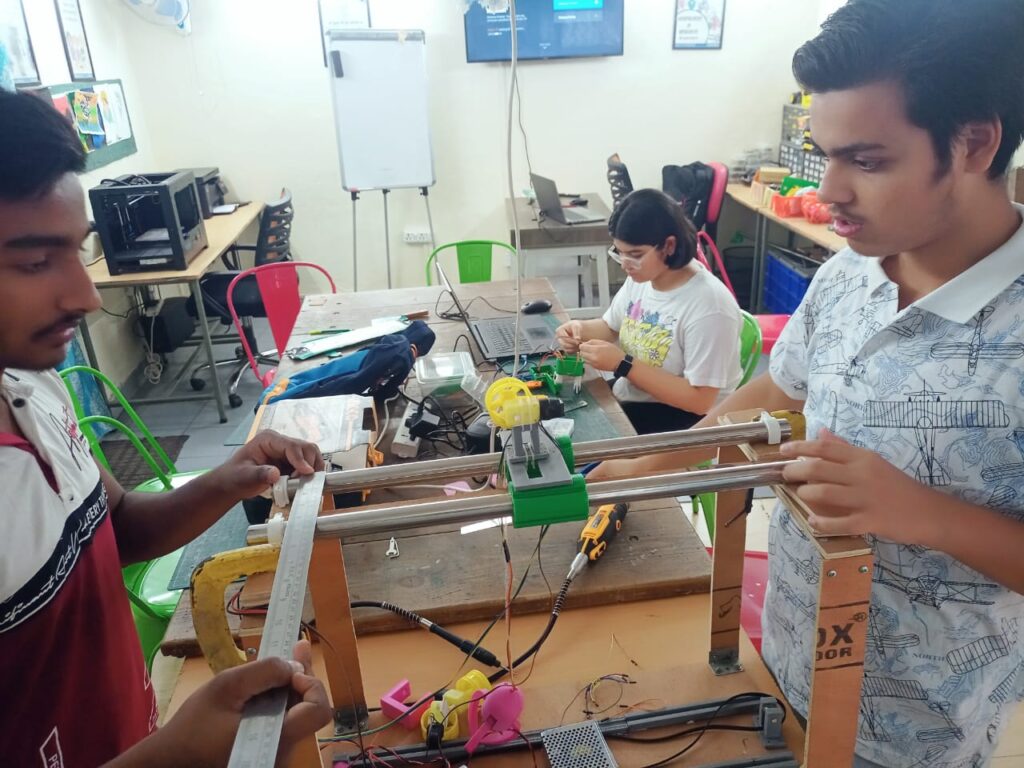

Unlocking potential through peer learning: where students thrive and grow together.
Flexible Education for Modern Learners: Adapting to Every Need

Flexible education adapts to diverse needs, offering online learning for accessibility and blended learning for balanced experiences.
Fix Education’s Gaps: Top Needs EdTech Must Solve
Apni pathshala Unmet educational needs which EdTech entrepreneurs need to address Our education system is a mess, and everyone seems to be paralysed into inactivity because it seems to be a wicked problem. The secret is to focus on one specific problem at a time – an unmet need – and provide the best possible […]
Transforming Education: Embracing DIY Learning

Apni pathshala Transforming Education: Embracing DIY Learning Education is no longer confined to classrooms and textbooks. A revolution is brewing, fueled by a powerful concept: DIY learning. This approach empowers students to take charge of their educational journey, fostering curiosity, independence, and a lifelong love of learning. Let’s delve into the world of DIY learning […]
The Art of Independent Study: Building Self-Reliance
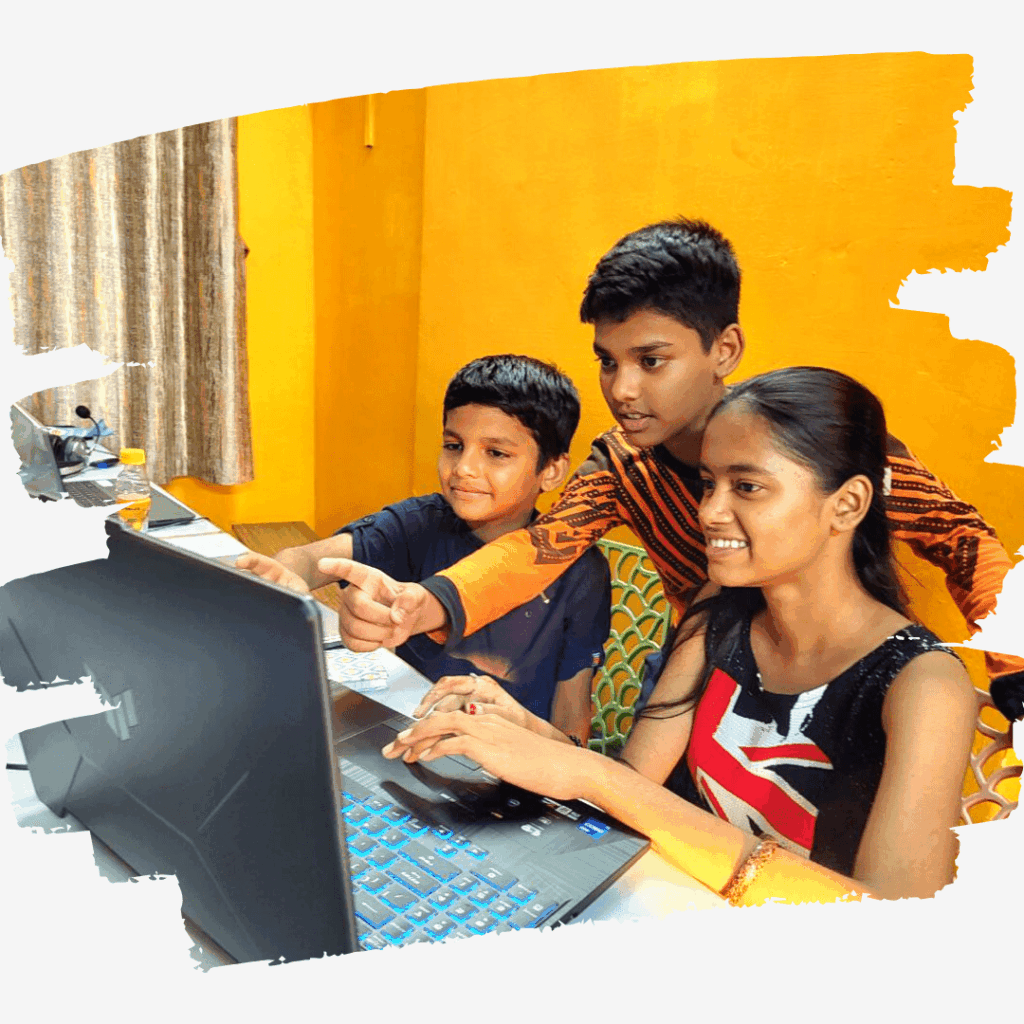

Mastering the art of independent study empowers individuals to take charge of their learning journey, fostering self-reliance and personal growth.
The Power of Peer Learning: Enhancing Education Together
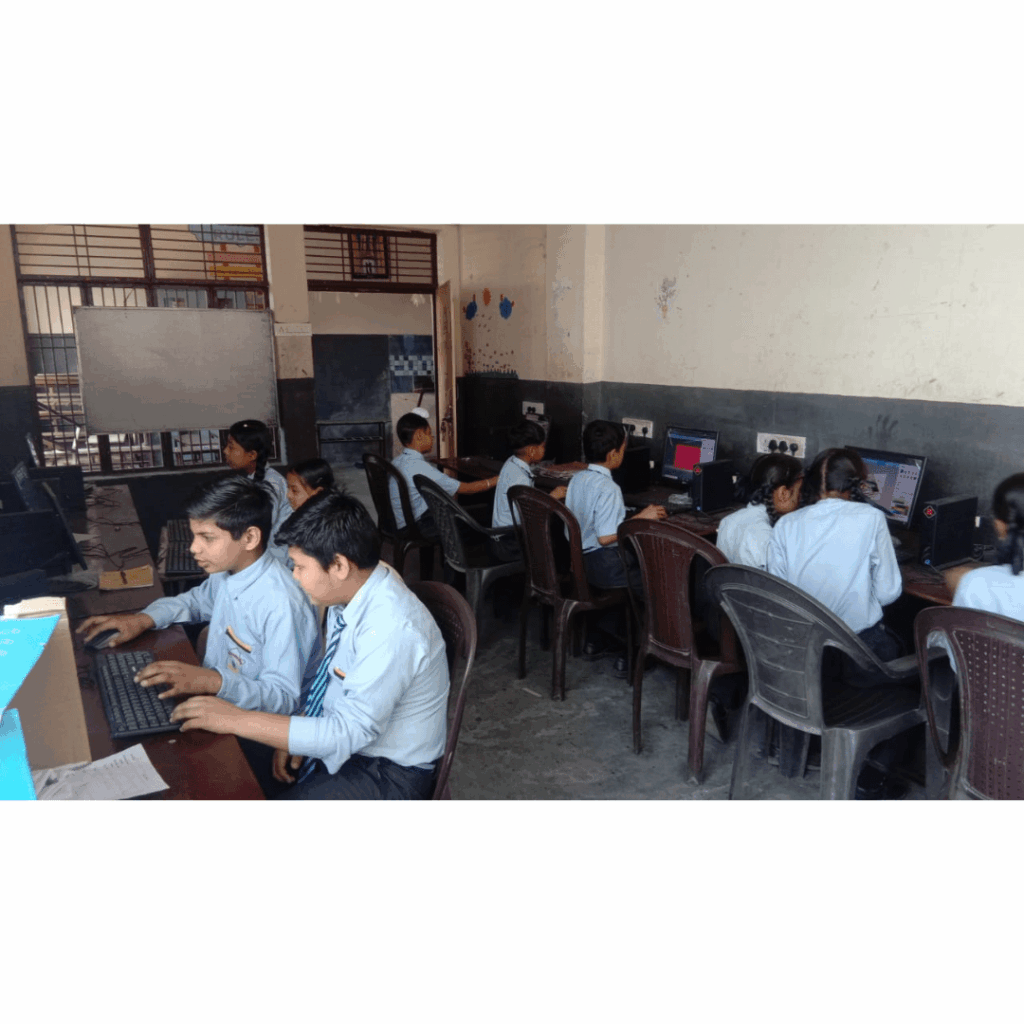

In the realm of education, a potent yet often underutilized tool lies within the dynamic interactions among students themselves. This resource is known as peer learning, a collaborative approach where students work together in groups to deepen their understanding of a subject or concept. Peer learning not only fosters academic growth but also cultivates essential […]
Hands-On Learning: The Power of Experiential Education
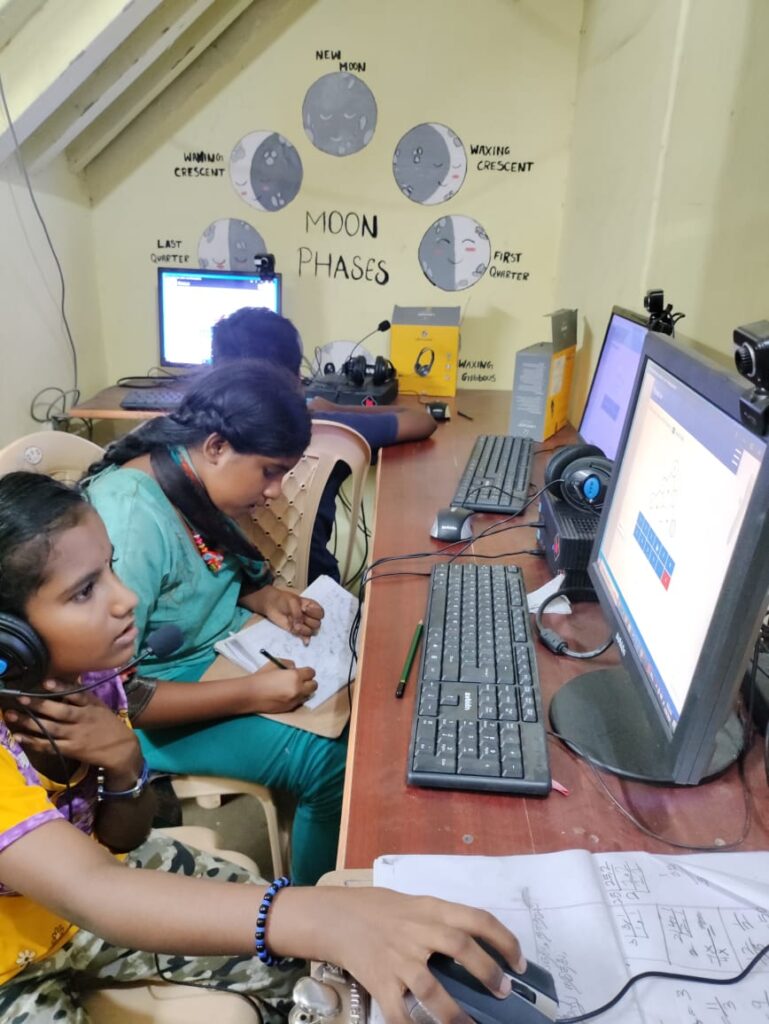

Apnipathshala Hands-On Learning: The Power of Experiential Education Experiential education involves immersive experiences that allow individuals to directly engage with the subject matter. Rather than passively absorbing information, students participate in activities that require active problem-solving and decision-making. Let’s Start In the realm of education, experiential learning has emerged as a transformative approach that goes […]